A polyline is a set of points defining the trajectory of a path.
Arguments
- ...
Various input for construction. See the Constructors sections
- id
An integer vector of the same length as
points, dividing the points into separate polylines (only used ifpointsis a point vector)- x
A
polyclid_polylinevector
Constructors
Providing a 2D points vector and no
idwill construct a single polylineProviding a 2D points vector and an
idvector will create a vector of polylinesInstead of a 2D point vector above you can provide x and y coordinates for the points directly.
Providing a list of 2D point vectors will construct a vector of polylines
See also
To get a complete overview of the boolean operations possible with polylines see the dedicated help page on the topic
Other polylines:
polyline_set()
Examples
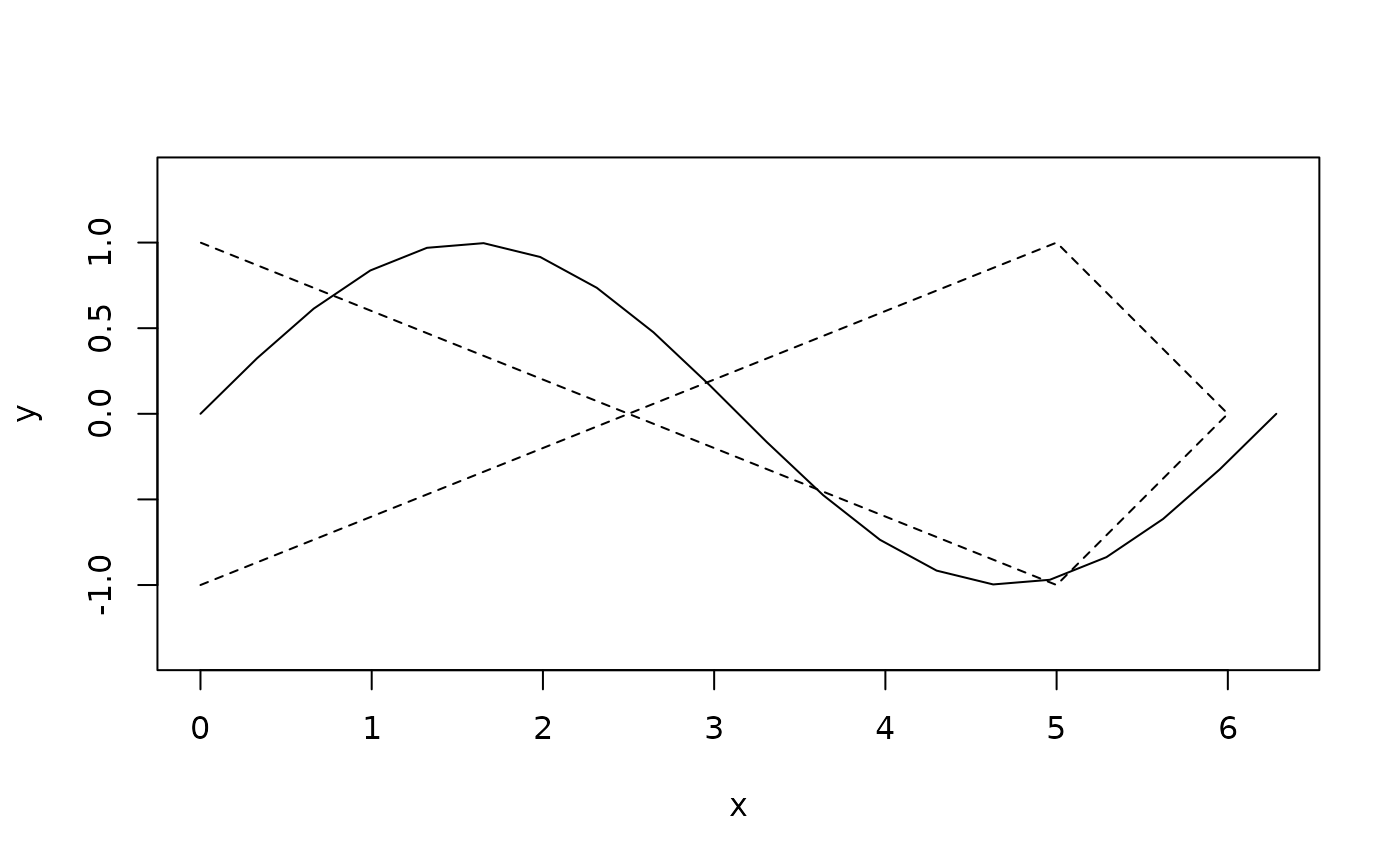
sine <- polyline(
seq(0, 2*pi, length.out = 20),
sin(seq(0, 2*pi, length.out = 20))
)
loop <- polyline(
c(0, 5, 6, 5, 0),
c(-1, 1, 0, -1, 1)
)
polylines <- c(sine, loop)
plot(polylines, lty = c(1, 2))
 is_selfintersecting(polylines)
#> [1] FALSE TRUE
# Polylines can also be reversed so they are traversed in the opposite
# direction
reverse_orientation(polylines)
#> <2D polyclid_polylines [2]>
#> [1] [Path: 20, Range: <<0, -0.997>, <6.28, 0.997>>]
#> [2] [Path: 5, Range: <<0, -1>, <6, 1>>]
is_selfintersecting(polylines)
#> [1] FALSE TRUE
# Polylines can also be reversed so they are traversed in the opposite
# direction
reverse_orientation(polylines)
#> <2D polyclid_polylines [2]>
#> [1] [Path: 20, Range: <<0, -0.997>, <6.28, 0.997>>]
#> [2] [Path: 5, Range: <<0, -1>, <6, 1>>]